Video RAM is the memory used by your Graphics Processing Unit to store the video data generated by it. The GPU is responsible for the images you can see on your display. All the data that are quickly needed by the GPU to process and display the images on your screen are stored in Video RAM.
If you are noticing buffering while using graphically intense programs, the issue is likely due to low VRAM storage. This issue can be fixed by increasing dedicated Video RAM on your device. In this article, I have discussed how to increase dedicated Video RAM on Windows 10 and 11.
Also check out:
Why Increasing Video RAM Will Help?
Contents
Video RAM or in other words VRAM is where all the graphical data is stored for displaying images on your screen. If VRAM is just like RAM but only the graphics related data is stored. It is built close to the GPU, to send the stored generated video data for faster processing.
Without the VRAM your system will have to depend on the RAM to also store the generated video data. This will make turn your PC slow and you will notice stuttering while playing graphics intense apps. The integrated GPU generally doesn’t have sufficient VRAM to run high graphics intensity apps. To do that you would need to buy a separate graphics card that comes with an allocated VRAM space.
If your PC is unable to run some high graphics intense games or videos, increasing the VRAM can help. But, how to get more dedicated Video RAM? Below I have discussed 2 methods, which can be used to increase the allocated Video RAM.
How To Increase Dedicated Video RAM?
There are 2 ways to increase dedicated video RAM on your PC. One way is by changing it from the BIOS and the other way is to use the Registry editor. But to increase the dedicated VRAM, you need to know what the allocated VRAM is on your PC. To find out the allocated VRAM space, follow the steps given below:
- Right-click on the start button to open the Power User’s Menu.
- Click on the Settings option.
- After the Settings app opens, click on the System option.
- Next, select the Display option from the left panel.
- Now on the right-panel, click on the Advanced Display Settings option in the Multiple Displays section.
- After that, click on the Display adapter properties option.
- In the Adapter tab, you will find the Total Available Graphics Memory information. It will be in the Adapter Information section.
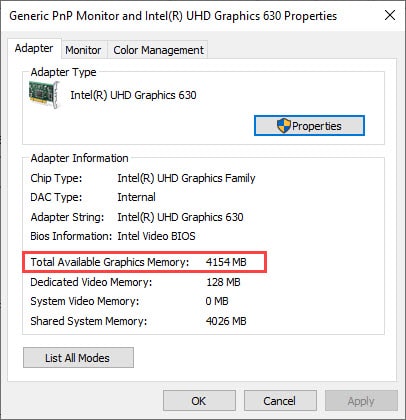
After you have seen how much VRAM is allocated in your PC, follow the methods to increase dedicated VRAM.
1) Increase Dedicated VRAM From BIOS
Increasing the dedicated VRAM from BIOS is the most optimal method out of the two. This is the first method you should try as it has a better chance of success. So, how to increase VRAM using BIOS? Follow the steps given below, to increase allocated VRAM from BIOS:
- First, restart your computer and press the BIOS key repeatedly. The BIOS key is generally F2, F5, F8, or Del key as it differs from PC to PC.
- Once you have entered BIOS, locate the Advanced option or something similar to that. Select it after you have found it.
- Next, click on the Graphics Settings option. Look for VGA Share Memory Size or Video Settings if the Graphics Settings option is unavailable.
- Set the dedicated VRAM to what you desire.
- Finally, save the configuration and again restart the PC.
Once your PC has restarted, check if the allocated VRAM has increased using the method given above. If you are not comfortable changing your BIOS settings, then try the next method.
2) Increase Dedicated VRAM From Registry (For Intel Integrated Graphics)
Increasing VRAM in integrated graphics is useless as the system will anyway reallocate the required space to process the extra generated video data. However, some apps will only run after it detects the required VRAM is available on your PC.
In such cases, you can use the Registry editor to increase the VRAM to fool these apps into working. However, this method only works for Intel integrated GPUs.
To increase the VRAM using Registry Editor, follow the steps given below:
- Press the Windows + R keys to open the Run utility.
- Type regedit in the search bar and press Enter to open Registry Editor.
- Navigate to the following location:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Intel - Right-click on the Intel Key and select the New option and then click on the Key option.
- Name the new key GMM.
- Select the GMM key and on the right panel, right-click on the empty area.
- Click on the New option and then select the DWORD (32-bit) Value option.
- Name the DWORD DedicatedSegmentSize.
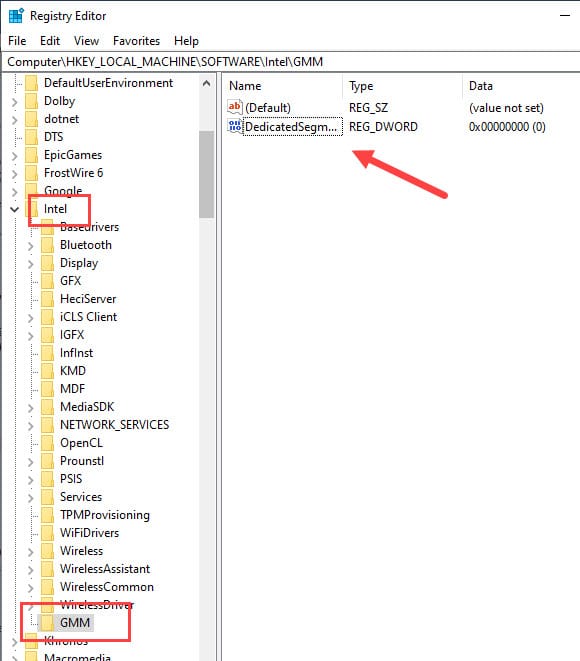
- Double-click on the DWORD you just created and change the Base to Decimal.
- Enter a value from 0 to 512, the value signifies the new allocated VRAM.
- Click on OK to save the changes.
- Finally, restart the computer.
After the computer restarts, you can check if the allocated VRAM has increased using the method given above.
Wrapping Up
So, that’s it. Now you know how to increase dedicated Video RAM on Windows 10. Before you try the above methods, it is advised that you read them carefully. Any mistake in the registry or BIOS can have serious consequences on your PC. Also, if you have any questions related to this topic, ask them in the comment section below.
Leave a Reply